# Objectives 目标
- Understand Uniform Distribution and Normal Distribution
了解均匀分布和正态分布 - Know how to generate the uniform and normal random numbers
知道如何生成均匀和正态随机数 - Know how to use
q-function to find the quantiles of the normal distribution
知道如何使用q-函数找到正态分布的分位数
# Uniform Distribution 均匀分布
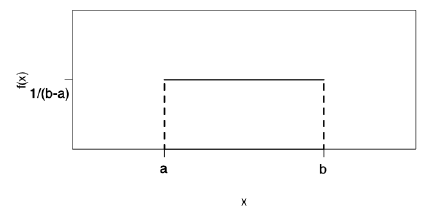
- Uniform Random Variable 均匀随机变量
- A uniform random variable is a continuous random variable for which every outcome in an interval is equally likely.
均匀随机变量是一个连续的随机变量,在一个区间内,每个结果的可能性都相等。
Example: is a random real number taken from .
是一个随机实数取自 。We can use
runif(n)to generate random number taken from .
我们可以runif(n)用来生成随机数取自 。
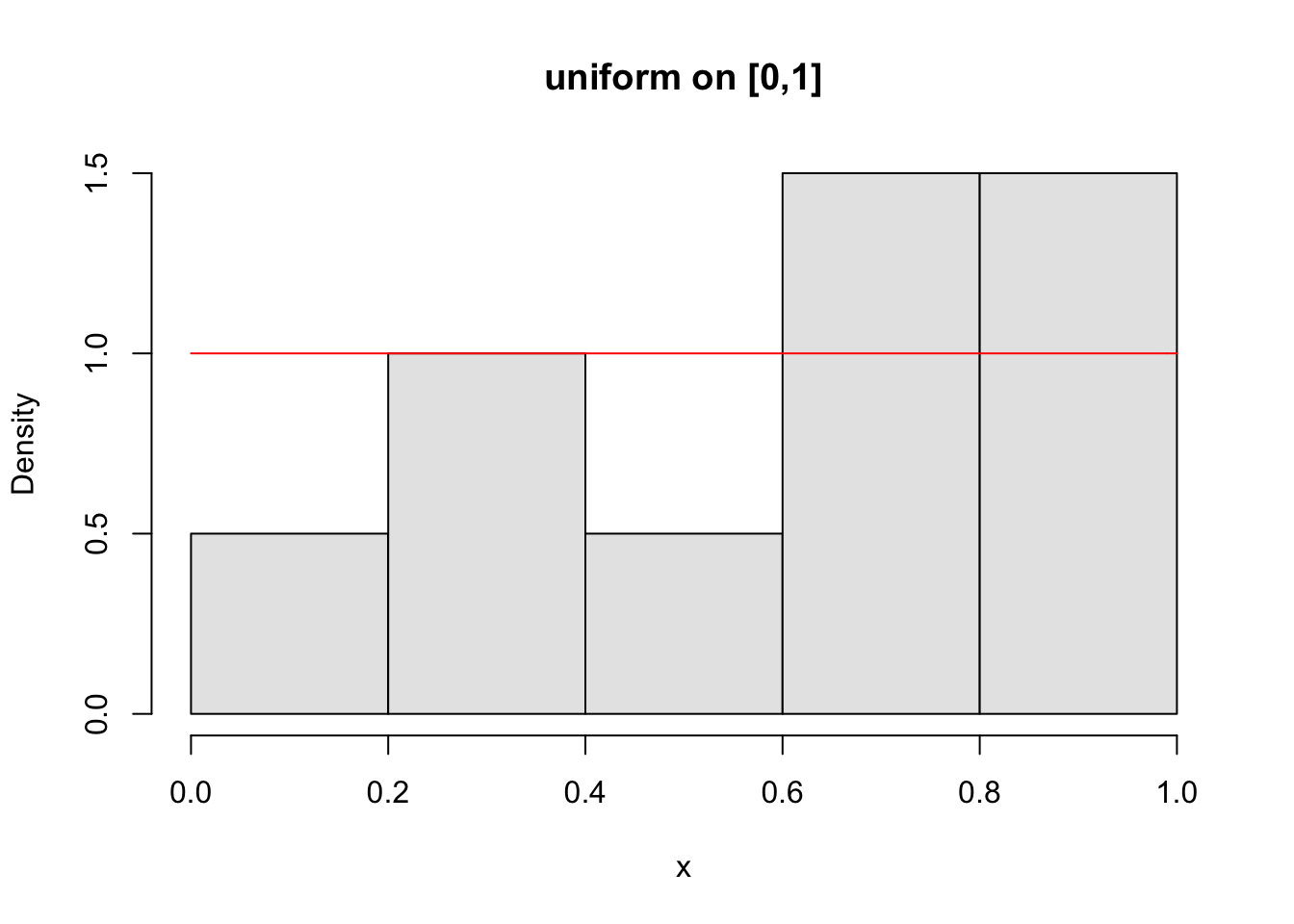
n <- 10 # number of sample size | |
x <- runif(n) # generate random numbers taken from the interval [0,1] | |
hist(x,probability=TRUE,col=gray(.9),main="uniform on [0,1]") | |
curve(dunif(x,0,1),add=T,col = "red") |
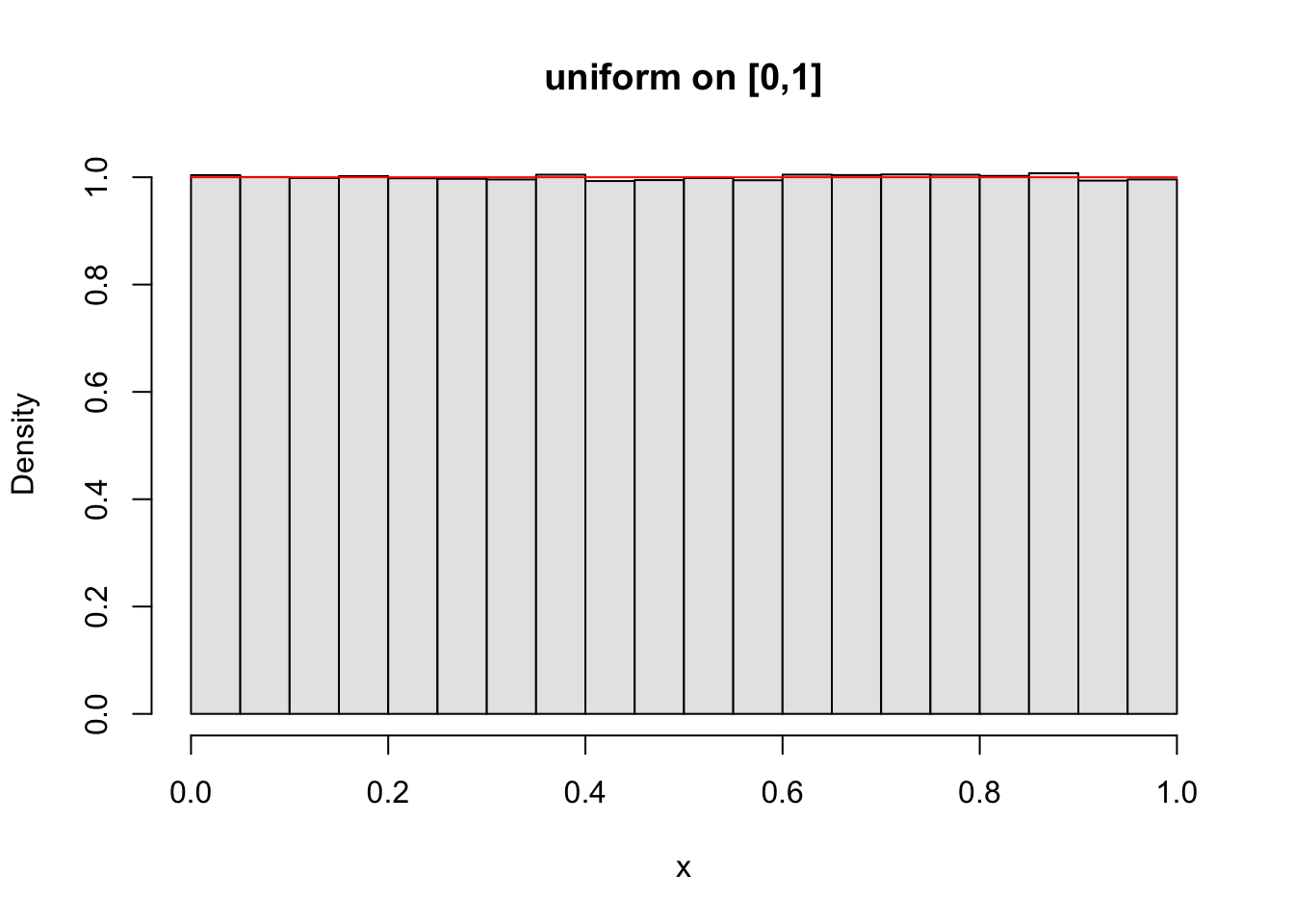
What will happen if increasing the number of the sample size?
如果增加样本数量会发生什么?
n <- 1e6 # number of sample size | |
x <- runif(n) # generate random numbers taken from the interval [0,1] | |
hist(x,probability=TRUE,col=gray(.9),main="uniform on [0,1]") | |
curve(dunif(x,0,1),add=T,col = "red") |
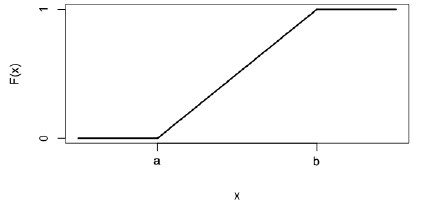
Notation:
Probability Density Function
pdf:
for
- Cumulative Distribution Function
cdf:
For
- Expectation & Variance 期望值与方差
# Important R functions
To generate random numbers, pdf (aka pmf), cdf, and quantiles.
生成随机数、pdf(又名 pmf)、cdf 和分位数。The prefixes for these functions are:
这些函数的前缀是:
r | random number generation | 随机数生成 |
d | probability density function or probability mass function | 概率密度函数或概率质量函数 |
p | cumulative distribution function | 累积分布函数 |
q | quantiles | 分位数 |
# Example 1
Suppose
n <- 1e6 # number of sample size | |
x <- runif(n,-1,1) # generate random numbers taken from the interval [-1,1] | |
hist(x,probability=TRUE,col=gray(.9),main="uniform on [-1,1]") # histogram of the relative frequency - probability=TRUE | |
curve(dunif(x,-1,1),add=T,col = "red") #plot the probability density function of X |
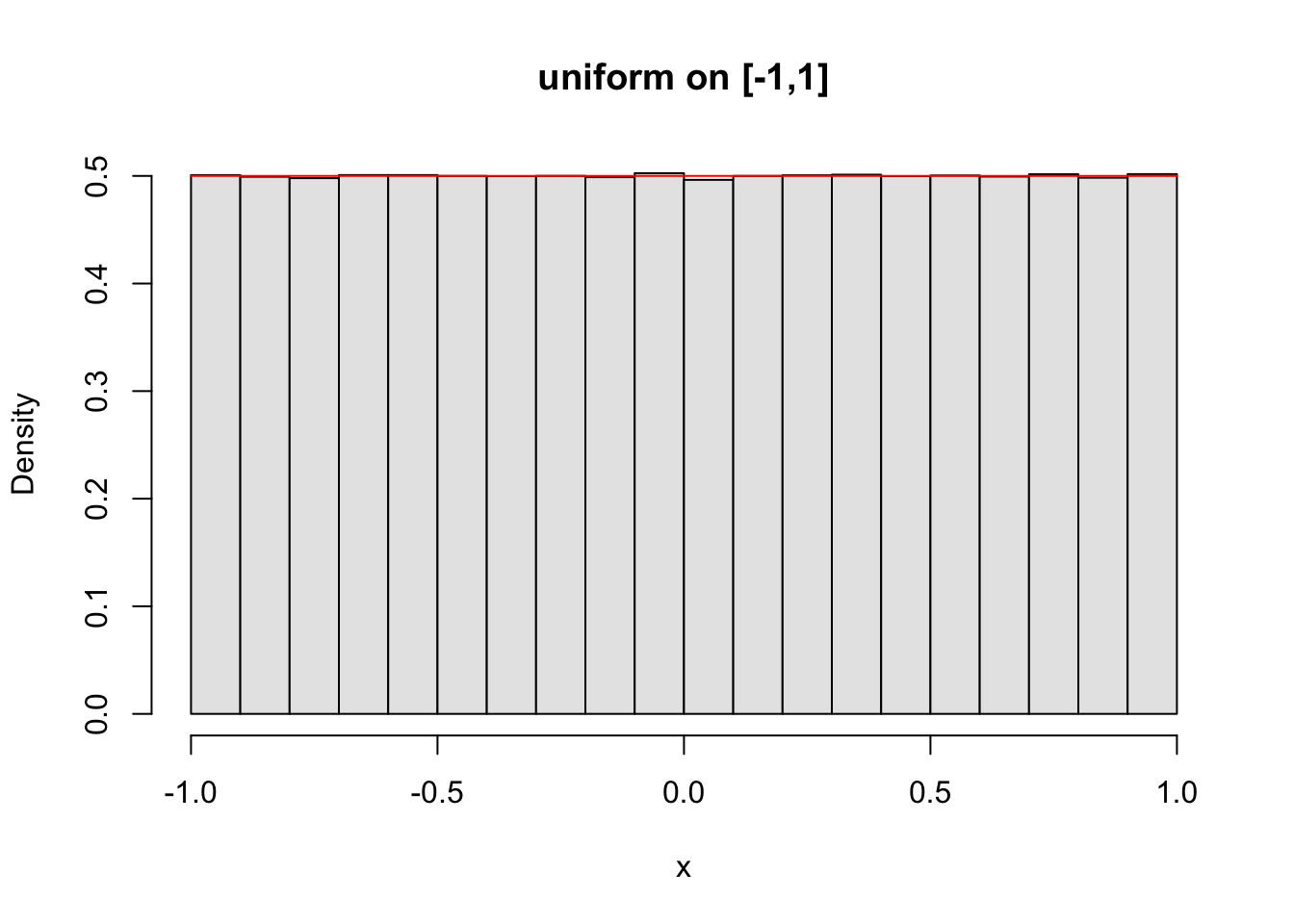
punif(0.5, min =-1, max = 1) # find the P(-1 <= X <= 0.5) |
[1] 0.75
qunif(0.5, min = -1, max = 1) # find the median of X |
[1] 0
mean(x) # find the sample mean |
[1] 0.0002108174
var(x) # find the sample variance |
[1] 0.3333544
# In-class Exercise: Uniform Distribution 均匀分布
Suppose , please generate the random numbers with sample size .
n <- 1e6 # number of sample size
x <- runif(n, -2, 3) # generate random numbers taken from the interval [-2,3]
Do a histogram for the instances you generated with the y-axis as relative frequency instead of frequency.
使用 y 轴作为相对频率而不是频率为您生成的实例绘制直方图。hist(x, probability=TRUE, col=gray(.9), main="uniform on [-2,3]") # histogram of the relative frequency
Find , , and (a little tricky).
punif(0, min =-2, max = 3) # find the P( X <= 0 )
[1] 0.4punif(1, min =-2, max = 3) # find the P( X <= 1 )
[1] 0.61 - punif(0, min =-2, max = 3) # find the P( X >= 1 )
[1] 0.4Find Q1, median, Q3 of this random variable . What is the expectation value and variance of ?
找到这个随机变量 的 Q1、中位数、Q3。期望值和方差是多少?qunif(0.25, min = -2, max = 3) # Q1
[1] -0.75qunif(0.5, min = -2, max = 3) # median
[1] 0.5qunif(0.75, min = -2, max = 3) # Q3
[1] 1.75The expectation is . The variance is .
Find Q1, median, Q3, mean, and variance of the sample you generated. Compare your results with the answers in Ex.4.
找出生成的样本的 Q1、中位数、Q3、均值和方差。将您的结果与例 4 中的答案进行比较。quantile(x)
0% 25% 50% 75% 100% -1.9999994 -0.7476943 0.5001483 1.7515364 2.9999982mean(x)
[1] 0.5008553var(x)
[1] 2.081609
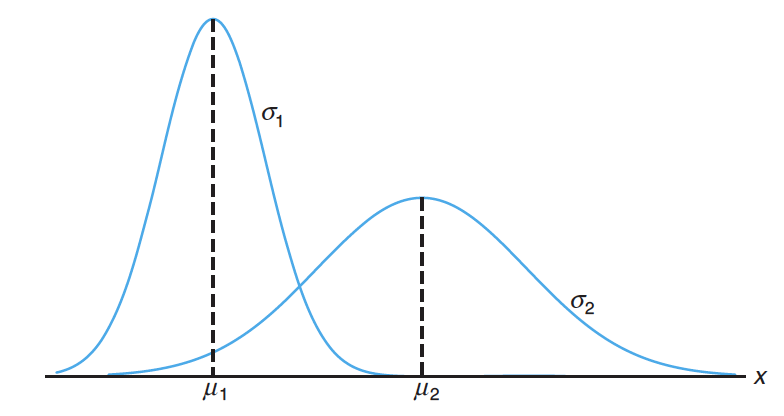
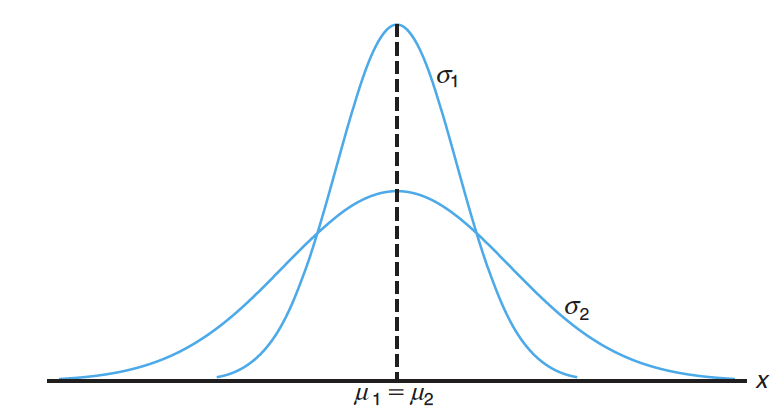
# Normal Distribution 正态分布
The normal distribution (also be called Gaussian distribution) is a symmetric distribution that is centered around a mean and spreads out in both directions.
正态分布(也被称为高斯分布)是围绕平均值和差居中出在两个方向上对称分布。Examples: Test scores for all ITM 514 students. 所有 ITM 514 学生的考试成绩。
Notation:
符号- is the mean of the distribution 分布的平均值
- is the variance of the distribution 分布的方差
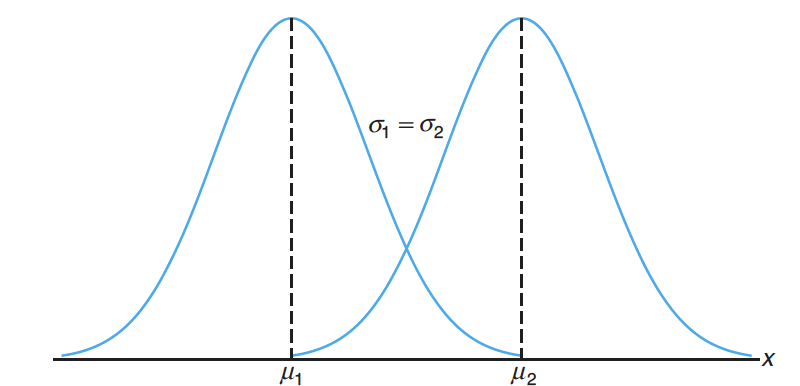
Probability Density Function
pdf:CDF: The CDF of normal distribution doesn't have a closed form, i.e., there is no analytic answer of the integral 正态分布的 CDF 没有封闭形式,即没有积分的解析答案
# Example 2
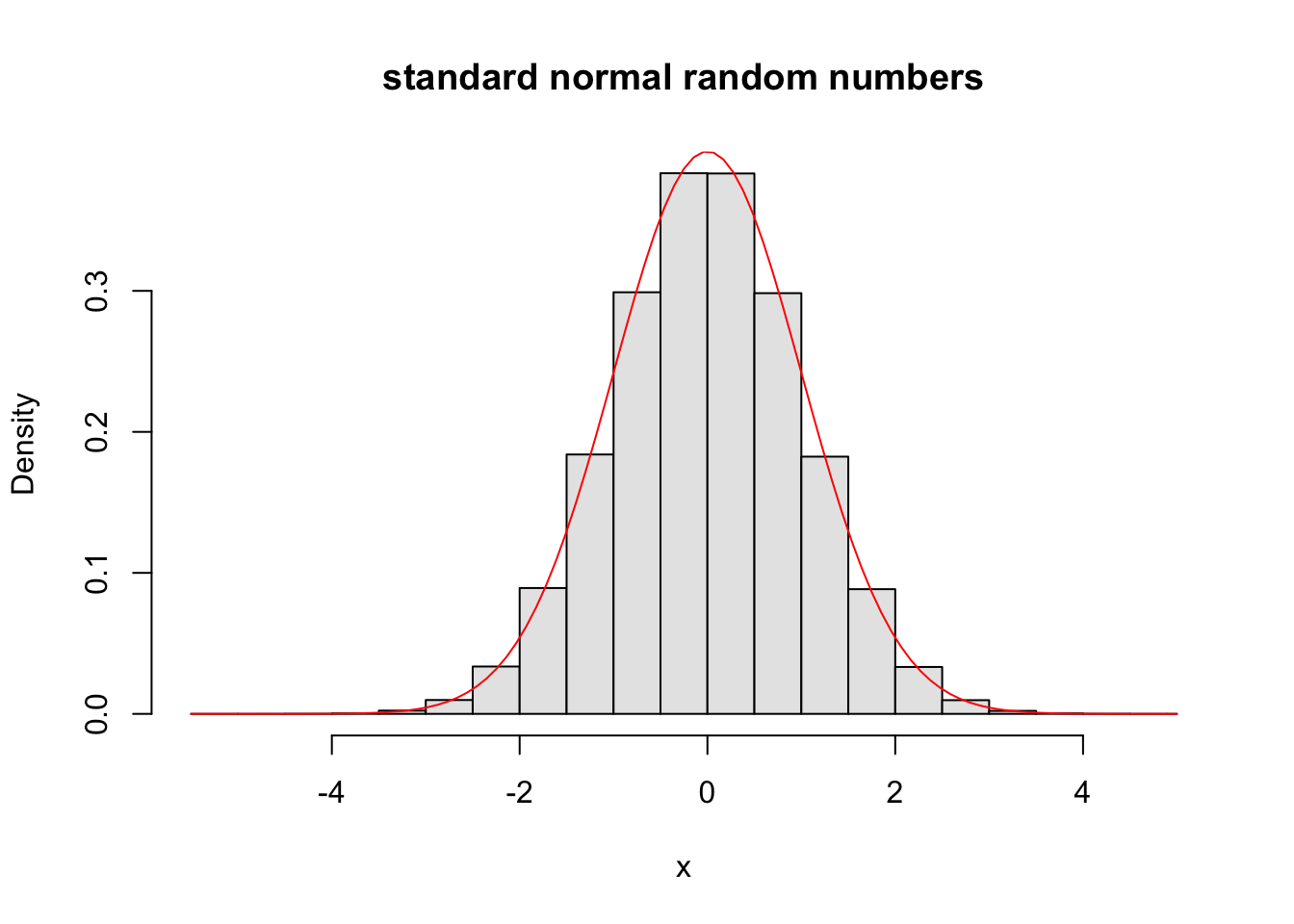
Suppose is the standard normal random variable, i.e.,
假设 是标准正态随机变量
n <- 1e6 # number of sample size | |
x <- rnorm(n, mean = 0, sd = 1) # generate the standard normal random numbers | |
hist(x, probability=TRUE, col=gray(.9), main="standard normal random numbers") # histogram of the relative frequency | |
curve(dnorm(x, mean = 0, sd =1),add=T,col = "red") #plot the probability density function of X |
pnorm(0.5, mean = 0, sd = 1) # find the P(X <= 0.5) or P(X < 0.5) |
[1] 0.6914625
qnorm(0.5, mean = 0, sd = 1) # find the median of X |
[1] 0
mean(x) # find the sample mean |
[1] -0.002525208
var(x) |
[1] 1.002635
What's the relationship between the general normal random variable and the standard normal random variable?
一般正态随机变量和标准正态随机变量有什么关系
To calculate the probability involving , 计算涉及的概率
\begin{eqnarray*} P(a\leq X\leq b) &=& P\left(\frac{a-\mu}{\sigma}\leq \frac{X-\mu}{\sigma}\leq \frac{b-\mu}{\sigma}\right)\\ &=& P\left(\frac{a-\mu}{\sigma}\leq Z\leq \frac{b-\mu}{\sigma}\right), \end{eqnarray*}# Example 3
The achievement scores from a college entrance examination are normally distributed with mean 75 and standard deviation 10. What fraction of the scores lies between 80 and 90?
高考成绩的平均分是 75,标准差是 10 的正态分布。80 到 90 之间的分数是多少?
The scores , then
p1<- pnorm(1.5, mean = 0, sd = 1) - pnorm(0.5, mean = 0, sd = 1) # find the P(0.5 <=Z <=1.5) | |
p1 # display the answer |
[1] 0.2417303
p2 <- pnorm(90, mean = 75, sd = 10) - pnorm(80, mean = 75, sd = 10) # find the P(80 <=X <=90) | |
p2 # display the answer |
[1] 0.2417303
# Example 4
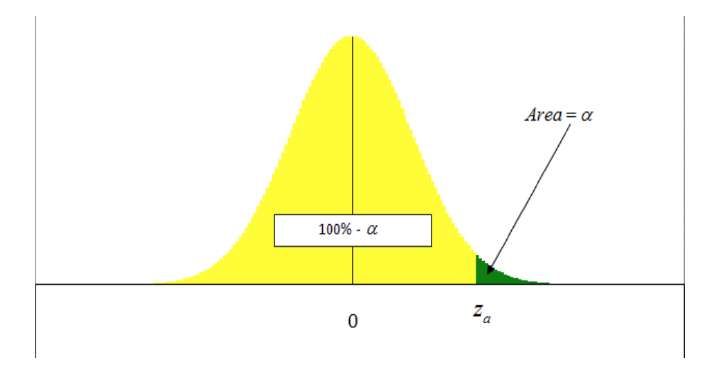
Find the value of such that of the standard normal values lie between and ; that is, .
找到 使 95 % 标准正常的 值介于 和 之间
How to find in R ?
p1 <- - qnorm(0.025, mean = 0, sd = 1) # find the P(0.5 <=Z <=1.5) | |
p1 # display the answer |
[1] 0.2417303
p2 <- pnorm(90, mean = 75, sd = 10) - pnorm(80, mean = 75, sd = 10) # find the P(80 <=X <=90) | |
p2 # display the answer |
[1] 0.2417303
# In-class Exercise
Suppose ,
can you find a such ?
假设 ,你能找到一个 且 ?
Critical value of a standard normal distribution is the value on the measurement axis for which of the are under the standard normal curve lies to the right of .
临界值 的标准正态分布是在测量轴上的值,对于这个 位于标准正态曲线下方的 。
# In-class Exercise: Normal Distribution
Suppose , please generate the random numbers with sample size .
认为 ,请生成样本大小的随机数 .#1 Create the samplen <- 1e6
x <- rnorm(n, mean = -1, sd = 3)
Do a histogram for the instances you generated with the y-axis as relative frequency instead of frequency.
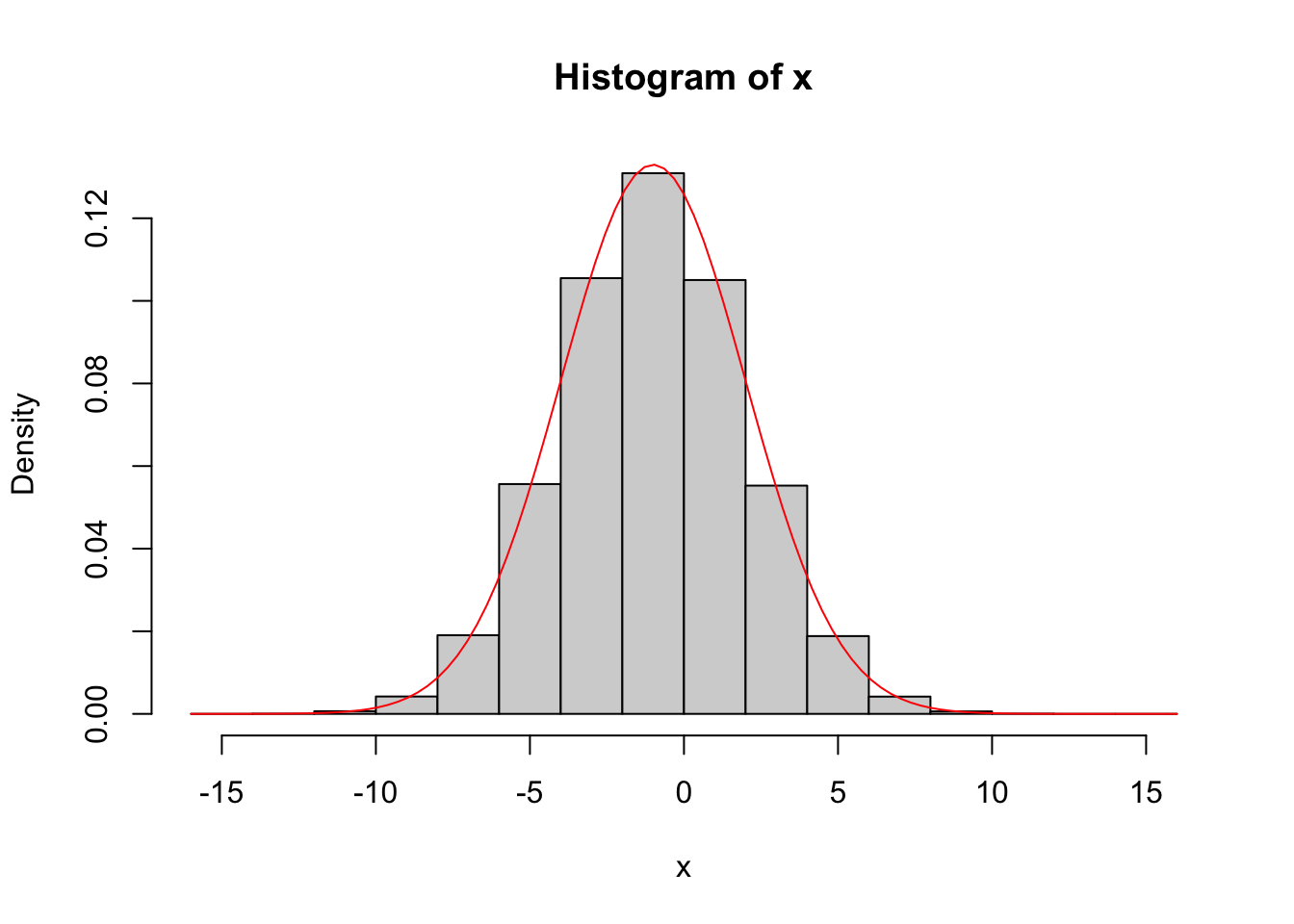
使用 y 轴作为相对频率而不是频率为您生成的实例绘制直方图。#2 A histogram of xhist(x, probability = TRUE)
curve(dnorm(x, mean = -1, sd = 3), add = T, col = "red")
![]()
Find , , , and .
找 , , , and 。#3 P(X <=0)pnorm(0, mean = -1, sd = 3)
[1] 0.6305587# P(X <= 1)pnorm(1, mean = -1, sd = 3)
[1] 0.7475075# P(X >= 1)1 - pnorm(1, mean = -1, sd = 3)
[1] 0.7475075# P(0 <= X <=1)pnorm(1, mean = -1, sd = 3) - pnorm(0, mean = -1, sd = 3)
Find Q1, median, Q3 of this random variable . What is the expectation value and variance of ?
找到这个随机变量 的 Q1、中位数、Q3, 的期望值和方差是多少 XX?#4 Q1qnorm(0.25, min = -1, max = 3)
[1] -3.023469#4 Medianqnorm(0.5, min = -1, max = 3)
[1] -1#4 Q3qnorm(0.75, min = -1, max = 3)
[1] 1.023469Find Q1, median, Q3, mean, and variance of the sample you generated. Compare your results with the answers in Ex.4.
找出您生成的样本的 Q1、中位数、Q3、均值和方差。将您的结果与第 4 题中的答案进行比较。#4 We know the mean is -1 and variance is 9#5 Q1, median, Q3 of the samplequantile(x)
0% 25% 50% 75% 100% -15.773765 -3.029712 -1.010223 1.014308 14.674138# Mean of the samplemean(x)
[1] -1.008806#5 Variance of the samplevar(x)
[1] 8.978004
# Conclusion
Normal distribution is the most important distribution. When we talk about the Central Limit Theorem, confidence interval, and hypothesis testing, we will come back to the normal distribution.
正态分布是最重要的分布。当我们谈论中心极限定理、置信区间和假设检验时,我们会用到正态分布。