# Components of Project Time Management 项目时间管理的组成部分
- Plan schedule management
计划进度管理 - Define activities
定义活动 - Sequence activities
序列活动 - Estimate activity resources
估算活动资源 - Estimate activity durations
估计活动时间 - Develop schedule
制定时间表 - Control schedule
控制进度
Defines how the schedule will be
- Developed
发达 - Managed
管理 - Executed
已执行 - Controlled
受控
- Developed
Defines schedule management approach for entire project
为整个项目定义进度管理方法
# Define activities
# Definition
- “Activity” 活动
- A distinct, scheduled portion of work performed during the course of a project.
在项目过程中执行的工作的明确的计划部分。
PMBOK, 6th ed. p. 698 - Schedule Management Plan 计划管理计划
- A component of the project management plan that establishes the criteria and the activities for developing, monitoring, and controlling the schedule.
项目管理计划的一个组成部分,用于建立用于制定,监视和控制进度的标准和活动。 - “Activity List” 活动列表
- A documented tabulation of schedule activities that shows the activity description, activity identifier, and a sufficiently detailed scope of work description so that project team members understand what work is to be performed.
计划活动的文档化表格,其中显示了活动描述,活动标识符以及足够详细的工作描述范围,以便项目团队成员了解要执行的工作。
PMBOK, 6th ed. p. 698 - “Define Activities” 定义活动
- The process of identifying and documenting the specific actions to be performed to produce the project deliverables.
识别和记录要为生成项目可交付成果而执行的特定操作的过程。
PMBOK 6th ed 704
# More on “Activities”
Work packages are: 工作包是:
- decomposed into activities,
分解成活动, - these then create the activity list
然后创建活动列表 - activity list items are then used to create the project schedule
活动列表项然后用于创建项目进度表
- decomposed into activities,
Activities typically have a “verb-noun” format; but this is not necessary
活动通常具有 “动词 - 名词” 格式;但这不是必需的Milestone activities typically have zero duration; but this is not necessary
里程碑活动的持续时间通常为零;但这不是必需的
Work Package vs Activity
# Contents of Define Activities 定义活动的内容
- Project work and project manager work
项目工作和项目经理工作 - Planning processes
规划过程 - Sequence of activities
活动顺序 - Procurement time
采购时间 - Internal and external events
内部和外部事件 - Known and unknown events
已知事件和未知事件
# Milestone 里程碑
“A significant event point or event in a project, program, …” (PMBOK 6th ed, p711)
“项目,程序中的重要事件点或事件……”
When adding a milestone to MS Project, we typically give it a duration of 0, and it typically marks the start or end of a group of related activities.
在向 MS Project 添加里程碑时,我们通常将其持续时间设置为 0,并且通常标记一组相关活动的开始或结束。
“Milestones are tools used in project management to mark specific points along a (project’s) timeline. These points may signal anchors such as a project start and end date, a need for external review or input and budget checks, among others. In many instances, milestones do not impact project duration (that is they often have a duration of zero). Instead, they focus on major progress points that must be reached to achieve success.”
“里程碑 是项目管理中用于标记(项目)时间轴上特定点的工具。这些点可能标志着锚点,例如项目的开始和结束日期,需要进行外部审查或进行投入和预算检查等。在许多情况下,里程碑不会影响项目的持续时间(也就是说,它们的持续时间通常为零)。相反,他们专注于取得成功所必须达到的主要进步点。”
Milestones are one of the tools that assist project managers to “determine whether or not the project is on schedule.”
里程碑是帮助项目经理 “确定项目是否如期进行” 的工具之一。
Some project managers use milestones only on the critical path. This practice can lead to the team ignoring non-critical path tasks during monitoring and controlling, which can lead to non-critical path items to putrefy and thus becoming problematic. The takeaway here is do not disregard tasks that are not on the critical path, or they can force themselves onto your critical path (in a bad way).
一些项目经理仅在关键路径上使用里程碑。这种做法可能导致团队在监视和控制过程中忽略非关键路径任务,这可能导致非关键路径项腐烂并因此成为问题。这里的要点是不要忽略不在关键路径上的任务,否则它们会迫使自己进入关键路径(以一种不好的方式)。
# Rolling Wave Planning 滚波计划
Imminent work planned out in more detail than distant work
即将进行的工作比远距离的工作更详细地计划
# Sequence Activities 序列活动
- Team activity
团队活动 - Establishing dependencies is VERY important
建立依赖关系非常重要 - People need to know who is counting on their ability to complete an activity and why.
人们需要知道谁在指望他们完成一项活动的能力以及原因。
# Mandatory vs. Discretionary dependencies 强制性与酌处性依赖关系
p. 191
- Mandatory 强制性
- “Legally or contractually imposed”
以法律或合同方式强加 - Discretionary Dependencies 可斟酌处理的依存关系
- based on organizational best practices
基于组织的最佳实践
# Reserves 储备
p. 202
- Contingency reserve 应急储备
- for identified risks
针对已确定的风险 - Management reserve 管理储备
- time set aside for currently unidentified risks.
为当前未识别的风险留出的时间。
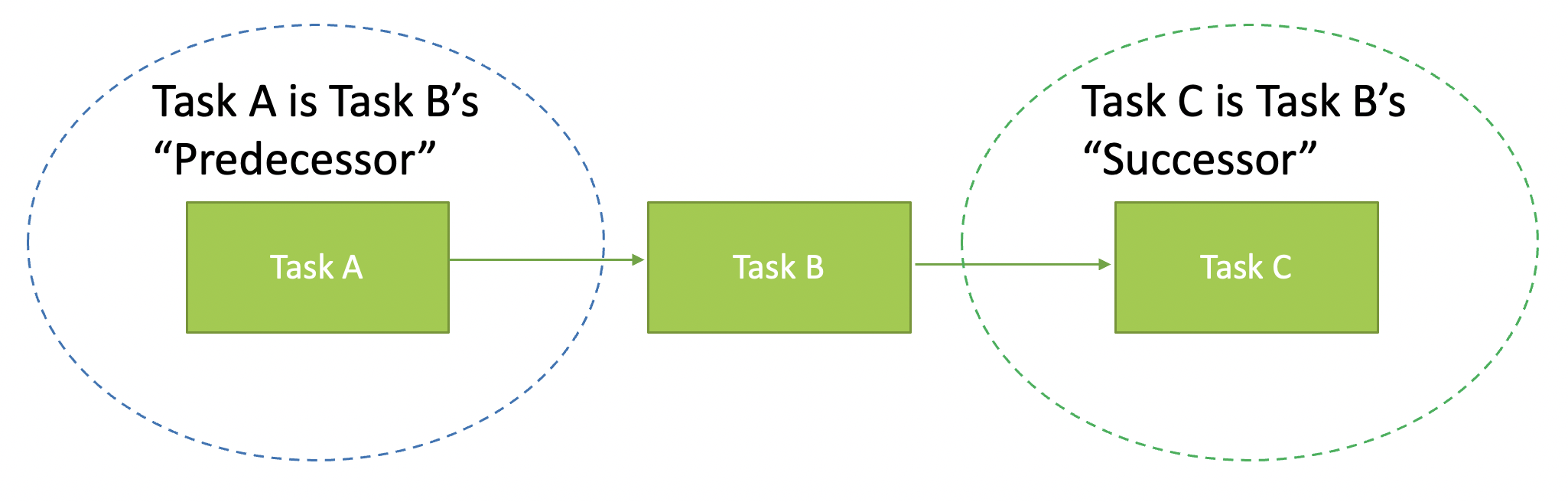
# Predecessor vs Successor 前辈 vs 后继
Given we are focusing on “Task B”;
鉴于我们专注于 “任务 B”;
“Task A” is the “predecessor of “Task B”, and “Task C” is the “Successor” of “Task B”
“任务 A” 是 “任务 B” 的 “前任”,“任务 C” 是 “任务 B” 的 “后继”
# Duration vs. Effort 持续时间与工时
Tom spends 2 hours every day for 5 days on activity#45
The duration of this task is: 5 days.
The effort is: 10 hours
- Effort and duration are not the same thing!
工时和持续时间不是一回事! - Duration is how long it takes your team to complete an activity. The more members on your team, until diminishing returns sets in, the shorter the duration.
持续时间是您的团队完成一项活动所需的时间。团队中的成员越多,直到收益递减到位,持续时间越短。 - Effort is how many hours you will bill to the project.
工作量是您需要向该项目计费的小时数。
Effort-hours = Team-member-#1’s-hours + Team-member-#2’s-hours + Team-member-#3’s-hours + Team-member-#4’s-hours …
工作时间 = 团队成员#1 的小时 + 团队成员#2 的小时 + 团队成员#3 的小时 + 团队成员#4 的小时…
# Precedence Diagramming Method 优先级图示方法
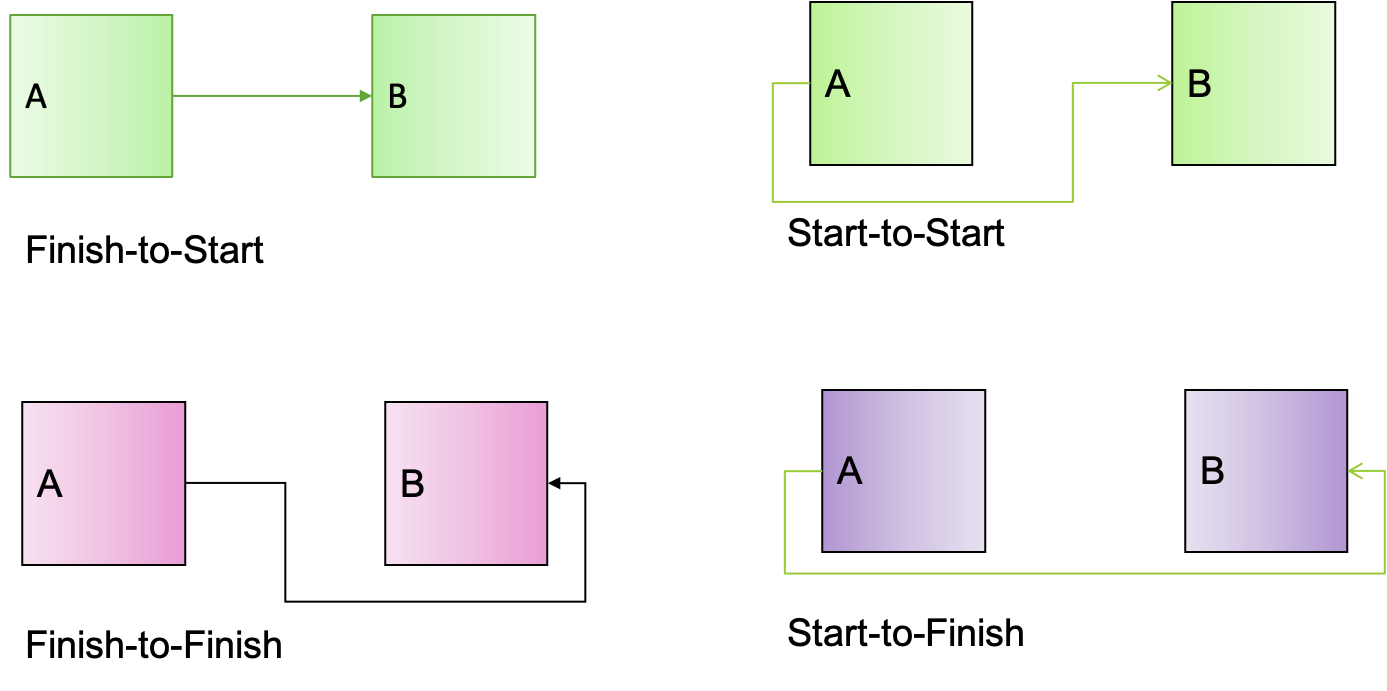
# Finish to Start 完成➡️开始
PMBOK 6th ed. P 190
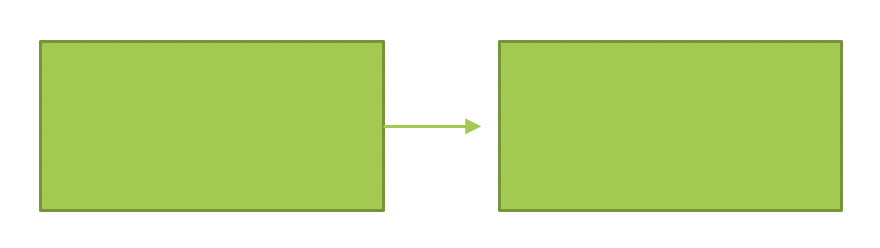
“A logical relationship in which a successor activity cannot start until a predecessor activity has finished. For example, installing-the-OS-on-a-PC(successor) cannot start until the PC-hardware-is-assembled(predecessor)”.
“一种逻辑关系,在此逻辑关系中,后续活动要等到先前活动完成后才能开始。例如,在组装 PC 硬件(前身)之前,无法在 PC 上安装 OS(后继产品)”。
This is the most common type
这是最常见的类型
# Start to Start 开始➡️开始
PMBOK 6th ed. P 190.
“A logical relationship in which a successor activity cannot start until a predecessor activity has started. For example, level concrete (successor) cannot begin until pour-foundation (predecessor) begins.”
“一种逻辑关系,在此逻辑关系中,后续活动要等到先前活动开始后才能开始。例如,在浇筑基础(前身)开始之前,水平混凝土(前身)才能开始。”
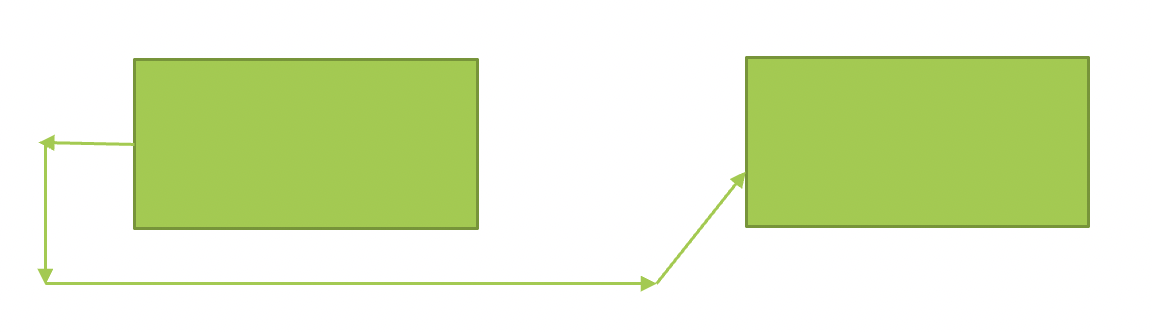
# Start to finish 开始到完成
PMBOK 6th ed. P 190
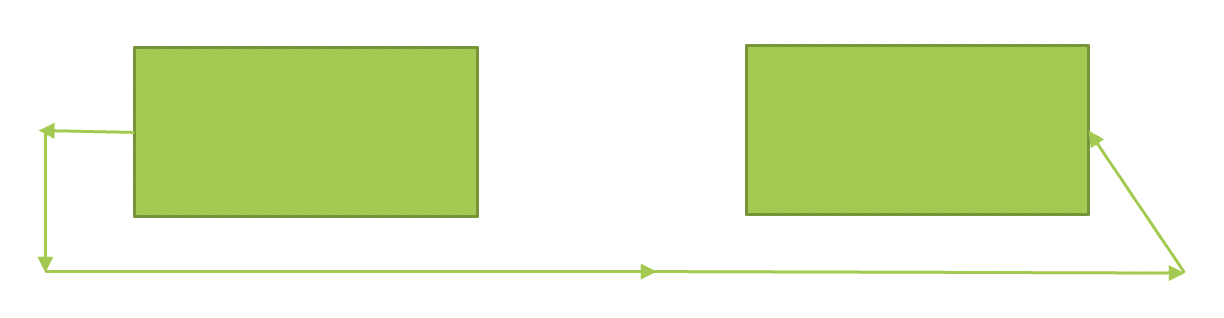
“A logical relationship in which a successor activity cannot finish until a predecessor activity has started. For example, a-new-accounts-payable-system (successor) has to start before the old-accounting-payable-system(can be shut down (predecessor).”
“一种逻辑关系,在这种逻辑关系中,接班人的活动要等到接班人的活动开始后才能完成。例如,新的应付帐款系统(后继系统)必须在旧的应付帐款系统(可以关闭(前身)之前)启动。”
“system” can be taken to mean “computer application”
“系统” 可以理解为 “计算机应用”
For further clarification see
# Finish to Finish 完成到完成
PMBOK 6th ed. p 190
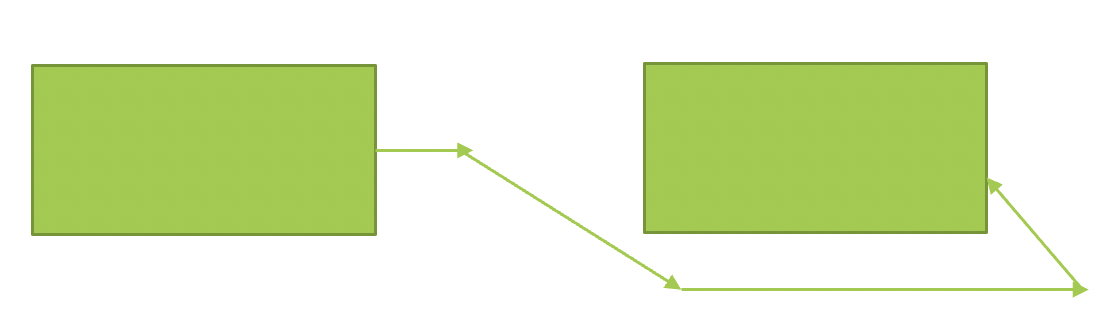
“A logical relationship in which a successor activity cannot finish until a predecessor activity has finished, For example, writing-a-document (predecessor) is required to finish before editing-the-document (successor) can finish”.
“一种逻辑关系,在该逻辑关系中,后续活动要在先前活动完成之前才能完成,例如,在完成对文档(继任者)的编辑之前,必须先完成文档编写(继任者)”。
# Critical path 关键路径
- The critical path has no free time on it.
在关键路径上有没有空闲时间。 - The Critical path identifies the minimum time that a project will take, and, the activities that compose the critical path.
在关键路径识别的最小时间,一个项目需要,并在此构成关键路径的活动。 - Activities that are not on the critical path(s) contain available time.
不在关键路径上的活动包含可用时间。
# Estimate Activity resources 估算活动资源
- Resources to complete activities
完成活动所需的资源 - People
人力 - Equipment
设备 - Materials
材料 - Facilities
设施
# Resource Availability Issues 资源可用性问题
- Negotiate for resources
协商资源 - Delay the activity or project
延迟活动或项目 - Find alternative resources
寻找替代资源
# Factors impacting estimation 影响估算的因素
p. 197
- Law of diminishing returns 收益递减法则
- at some point more inputs do not create more outputs, and if taken to an extreme, even more inputs can reduce overall output.
在某些时候,更多的投入不会创造更多的产出,而如果将其推高至极点,甚至更多的投入都会减少总体产出。 - Number of resources 资源数量
- Adding more resources can increase risk
添加更多资源会增加风险 - Advances in technology 技术进步
- Can reduce duration estimates
可以减少工期估算 - Motivation of staff 员工激励
- Parkinson’s law: Work tends to expand to fill the time available
帕金森定律:工作趋于扩大以填补可用时间 - Procrastination: teams can postpone significant effort until the due date.
拖延:团队可以将大量精力推迟到到期日。
- Parkinson’s law: Work tends to expand to fill the time available
# Analogous Estimating 类比估算
- Creates an analogy
产生一个类比 - Similar project work
类似项目工作 - Historical information
历史资料 - Top-down estimating
自上而下的估算
# Parametric Estimating 参数估算
- Parameter for estimating
估计参数 - Repetitive work
重复性工作
“An estimating technique in which an algorithm is used to calculate cost or duration based on historical data and project parameters.” Regression analysis is good for this.
“一种估算技术,其中使用一种算法根据历史数据和项目参数来计算成本或工期。” 回归分析对此很有帮助。
# Three-Point Estimates 三点估算
- Finds an average of
求平均值- Optimistic
O
乐观的 - Most likely
ML
最有可能的 - Pessimistic
P
悲观 - Also called triangular distribution
也称为三角分布
- Optimistic
(O+ML+P)/3=estimate
(25+45+75)/3=48.33 hours
# PERT Estimates PERT 估算
- Program Evaluation and Review Technique
计划评审技术 - Also called beta distribution
也称为 Beta 分布
(O+(4ML)+P)/6=estimate
(25+(4x45)+75)/6=46.66 hours
# Develop Schedule 制定时间表
- Defines the sequence of events
定义事件的顺序 - Durations of the activities and project
活动和项目的持续时间 - Determines when resources are needed
确定何时需要资源 - Establishes logical relationships between activities
建立活动之间的逻辑关系
# Risks and the Schedule 风险与时间表
- Risk is an uncertain event or condition
风险是不确定的事件或状况 - Knowns and unknowns
已知与未知 - Risk analysis affects completion
风险分析影响完成 - Risk affects costs and time
风险影响成本和时间
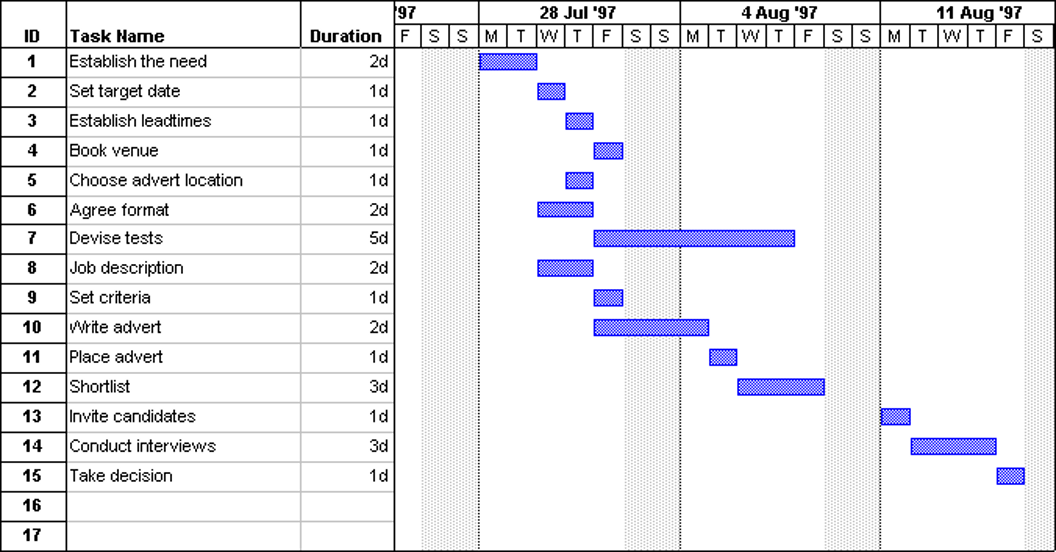
# Determining the Project Timeline 确定项目时间表
Gantt charts are pretty typical. This looks very similar to the default on MS Project.
甘特图非常典型。这看起来非常类似于 MS Project 上的默认设置。
# Using Resource Leveling Heuristics 使用资源均衡启发法
- Limits labor in time period
限制时间劳动 - Often extends the project schedule
通常会延长项目进度
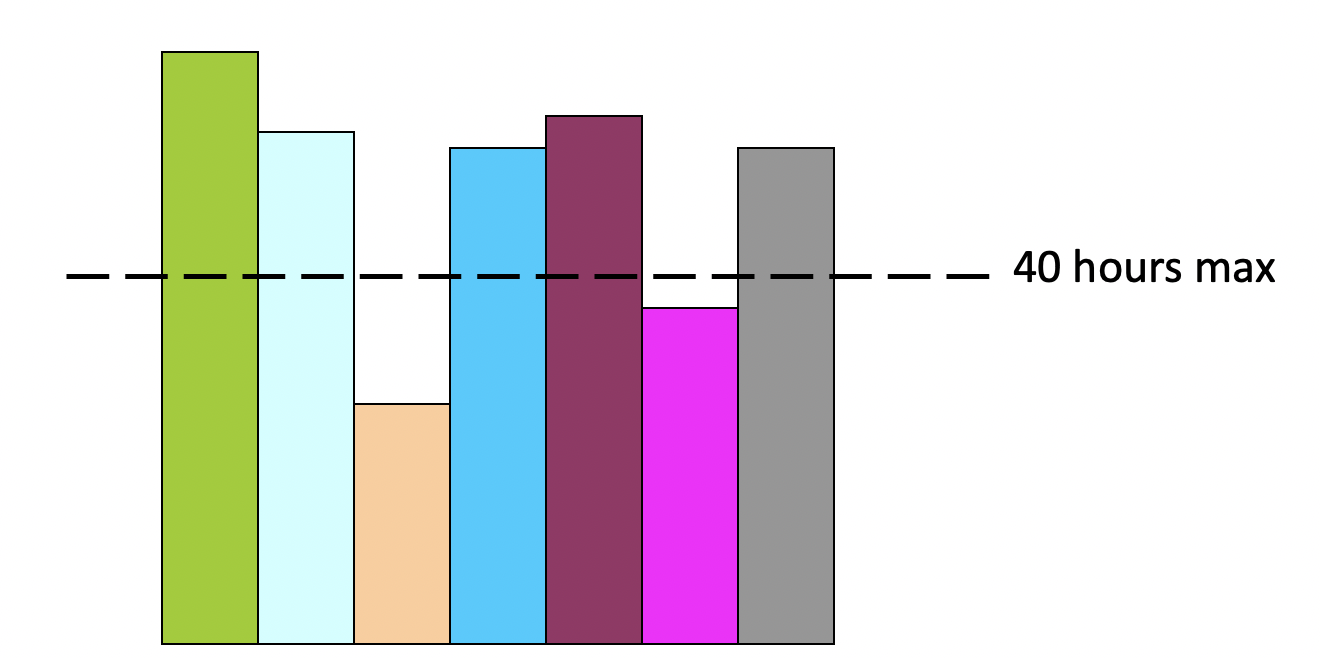
# Critical path defined 定义的关键路径
- The sequence of activities determining the minimum time for the project to complete
确定项目完成最短时间的活动顺序 - Give all the possible paths through the Gantt Chart to complete a project, this is the longest of all the possible paths.
通过甘特图给出所有可能的路径以完成一个项目,这是所有可能的路径中最长的。
Example: if you add one day to the duration of the critical path, you add one day to the duration of the project.
示例:如果将关键路径的持续时间增加一天,则将项目的持续时间增加一天。
# Schedule Compression 进度压缩
# Crashing (important) 赶工
Crashing adds recourses (staff, hardware, etc.), at an additional cost to the project, to the critical path to reduce the duration of the project. A caution here is that after some point, either diminishing returns will set in, or, you will have another critical path (that you will then need to crash)
赶工,将资源(人员,硬件等)添加到项目的关键路径上,以减少项目的工期,但要为此增加额外的成本。这里要注意的是,在某个时候之后,要么是收益递减,要么是您有另一个关键路径(然后您需要崩溃)Crashing (p 703 6th ed. PMOBOK) “A technique used to shorten the schedule duration for the least incremental cost by adding resources.”
“一种通过添加资源来以最小的增量成本来缩短计划持续时间的技术。”Fast tracking overlaps project schedule paths to reduce the overall duration of the project. This typically results in no increased costs; but often creates extra risk.
快速跟踪与项目进度路径重叠,以减少项目的总体持续时间。这通常不会导致成本增加;但通常会带来额外的风险。
# Fast Tracking (important) 快速跟踪
Fast tracking overlaps project schedule paths to reduce the overall duration of the project. This results in no increased costs
快速跟踪与项目进度路径重叠,以减少项目的总体持续时间。这样就不会增加成本Fast Taking (PMBOK 6th Ed, p. 706): “A schedule compression technique in which activities or phases normally done in sequence are performed in parallel for at least a portion of their duration”
“一种时间表压缩技术,其中通常按顺序进行的活动或阶段在其持续时间的至少一部分时间内并行执行”
# Measuring project performance 衡量项目绩效
- Value tied to percentage of work completed
价值与完成的工作百分比相关 - Planned value – what the project should be worth
计划价值–该项目应该值多少钱 - Estimate to complete
估计完成 - Milestones
里程碑 - Key deliverables
主要成果